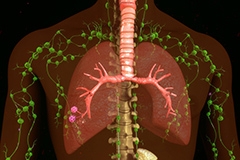
Cancer in the Lymph Glands: Risk Factors, Symptoms & Treatments
Medically Reviewed by Sreenivas V. Rao, MD
Lymphoma represents one category of cancer cells that can be effectively treated with chemotherapy. The treatment of lymphomas has markedly improved due to the addition of antibodies targeted against the lymphoma cells.
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymph glands and there are many kinds of lymphomas. Their course varies with some growing very slowly and others progressing very rapidly.
RISK FACTORS
Most lymphomas occur spontaneously, but there are certain populations at higher risk for lymphoma. Lymphomas are more likely to affect patients with autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren’s disease or patients who have organ transplants. Patients with viral exposure such as Hepatitis C and HIV are also more prone to develop lymphoma. Additionally, some research shows a connection between environmental exposures and lymphoma and there have been associations noted with toxins and chemicals in herbicides.
LYMPHOMA SYMPTOMS
Common symptoms of lymphoma are enlarged lymph glands. A person might notice swelling in the neck, armpit or even in the groin. During a medical exam, a physician can check these areas and discover the lymph node enlargement. However, there can be swollen lymph nodes all over the body including inside the abdominal cavity and the chest that we can usually not find on a physical exam. The other prominent symptoms of lymphoma are weight loss without a clear cause, unexplained chills or fever or drenching night sweats. These symptoms are collectively called the B-symptoms.
IS AGE A FACTOR?
We tend to see lymphoma in all age groups. We see some types of lymphoma in the younger adult age group, but the elderly population can also be affected especially with Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
HAVE A QUESTION?
-
McLEOD REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER FLORENCE
843-777-2000 -
McLEOD DARLINGTON
843-777-1100 -
McLEOD DILLON
843-774-4111 -
McLEOD LORIS
843-716-7000 -
McLEOD SEACOAST
843-390-8100 -
McLEOD CHERAW
843-537-7881 -
McLEOD CLARENDON
803-433-3000


-
McLEOD REGIONAL MEDICAL CENTER FLORENCE
843-777-2000 -
McLEOD DARLINGTON
843-777-1100 -
McLEOD DILLON
843-774-4111 -
McLEOD LORIS
843-716-7000 -
McLEOD SEACOAST
843-390-8100 -
McLEOD CHERAW
843-537-7881 -
McLEOD CLARENDON
803-433-3000
 Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor  Locations
Locations  Services
Services